Customized Metal 3D Printing Service
High-quality prototypes and manufacturing parts.

Metal 3D Printing Service online
What is Metal 3D Printing?
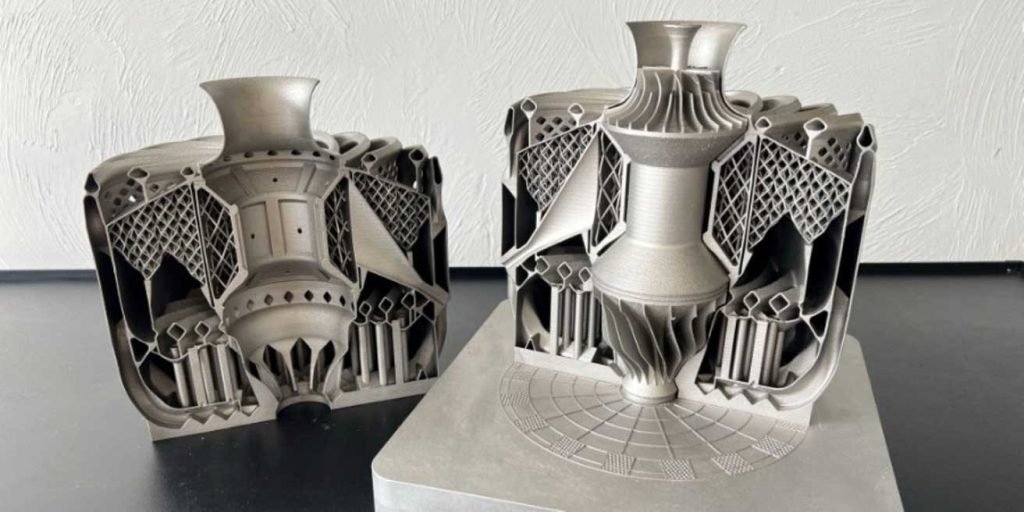
Metal 3D printing, an additive manufacturing technique, creates components by melting metal particles layer by layer to form a metal piece. It is frequently selected as a substitute for CNC machining or metal casting due to its ability to manufacture parts with the robustness and longevity of metal, while also benefiting from the design flexibility provided by 3D printing. This method enables the production of intricate designs such as lattices and topology-generated structures, both of which are unachievable through conventional CNC machining.

Benefits of Metal 3D Printing
Metal 3D printing offers numerous advantages, as it is capable of creating intricate metal components with high performance characteristics suitable for various applications. These 3D printed metal parts exhibit isotropic properties, ensuring uniform strength in all directions, and possess exceptional mechanical attributes akin to metals such as aluminum, stainless steel, titanium, Inconel, tool steel, and stainless steel-bronze composites.
Moreover, 3D metal printing enables the consolidation of multiple assembly components into a single part, resulting in a more robust structure that minimizes potential failure points associated with threads and inserts.
By directly transmitting CAD file data to the printer, metal 3D printing streamlines the production process, making parts more cost-effective and quicker to manufacture compared to machined metal parts. Machining metal components involves additional expenses like tooling set-up and longer processing times, whereas most 3D printed metal parts can be completed in less than a week.
Which one to choose:
DMLS or Binder Jet Metal?
Discover the exceptional 3D metal printing services offered by MXY, which encompass the advanced techniques of direct metal laser sintering (DMLS) and metal binder jetting. With these advanced processes at your disposal, you can effortlessly bring your metal prototypes, tooling, and production parts to life whenever you need them. It’s important to note that each of these remarkable 3D printing methods utilizes distinct metals and fusion techniques, ensuring that the resulting parts possess unique mechanical properties, pricing options, and lead times.

Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS) Overview
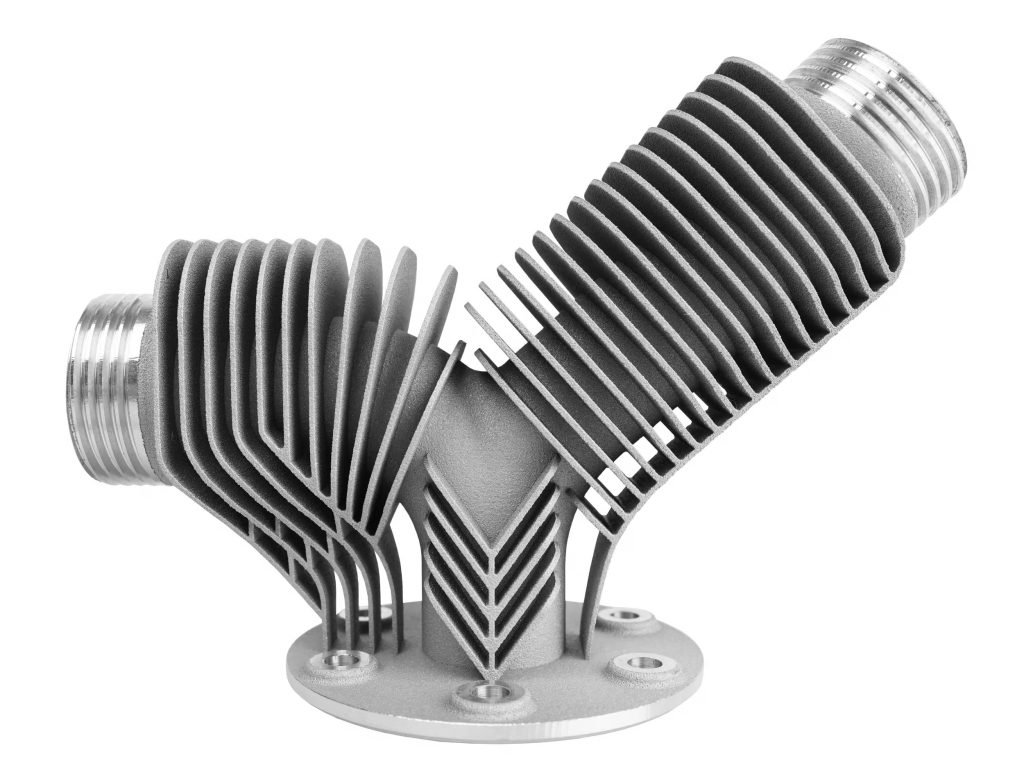
DMLS, or selective laser melting (SLM), involves using a laser to selectively fuse portions of fine metallic powder layer by layer. DMLS offers the benefit of creating fully dense components suitable for fluid transfer purposes. Materials such as aluminum AlSi10Mg, stainless steel, maraging steel, tool steel, cobalt chrome, and Inconel can be utilized in DMLS. While more costly than binder jetting, DMLS boasts superior mechanical characteristics ideal for high-precision uses.

Binder Jet 3D Printing Overview
Metal binder jetting is a multi-step process where a binding agent is selectively deposited onto a metal powder bed, layer by layer, to maintain the metal powder in a 3-dimensional shape. The resulting shape is then cured and placed into a furnace for sintering or infiltration with bronze. Parts created through binder jetting with overhanging features are supported by loose powder on all sides, typically eliminating the need for post-processing.
Binder jetting is a popular choice for metal 3D printing due to its cost-effectiveness and speed, allowing for high-volume production. Metal parts produced through binder jetting are ideal for functional prototypes or end-use parts with a density of approximately 95% or higher. Artists and hobbyists also favor metal binder jetting for its ability to create intricate features at a lower cost compared to DMLS or machining. However, unlike DMLS, binder jet parts may experience shrinkage, so engineers should consider design-for-manufacturing principles when creating parts, such as scaling CAD models by 1-2% and enlarging holes.

Material Properties of Direct Metal Laser Sintering
- Stainless Steel 17-4
- Stainless Steel 316/L
- Aluminum AlSi10Mg

Material Properties of Metal Binder Jetting Material
- Metal 420i (420 stainless infiltrated with bronze)
- All finishes available
Metal 3D Printing Applications Across Different Sectors
Metal 3D printing is a versatile technology that finds applications in various industries. In rapid industrial tooling, it is utilized for creating parts with intricate designs and thin walls, such as conformal jigs, fixtures, stamps, dies, and cutting inserts. On the other hand, in industries like consumer products, robotics, aerospace, and defense, metal 3D printing is employed for producing components with integrated fastening features, end-effectors, and metal lattice structures. The durability and strength of metal 3D printed parts make them suitable for use in fully functional late-stage prototypes or end-use parts across a wide range of applications.
Metal 3D Printing applications
Models Depicting Concepts
Product developers can easily produce physical prototypes of their designs using plastic 3D printing, thanks to its speed and versatility in the iterative process.
Rapid Prototyping
Plastic 3D printing enables the production of functional plastic prototypes, including moving parts and all-in-one assemblies.
Digital Production Directly
Plastic 3D Printing is perfect for creating numerous customized or individual parts due to its exceptional precision and reliability.
Why choose mXY

Endless choices
Select from a wide range of options for your order, including various materials, finishes, tolerances, markings, and certifications.

User-friendly
Have your parts conveniently delivered to your doorstep, eliminating the need for sourcing, project management, logistics, or shipping.

Verified Network
Our certifications include ISO 9001:2015, ISO 13485, and AS9100D. Only the best shops that meet our standards become Suppliers.
